Robust and reliable
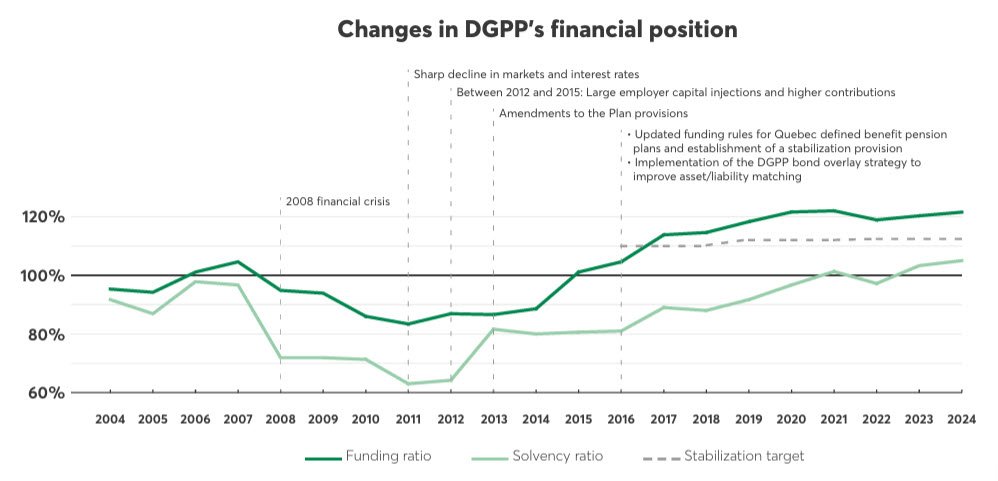
Once again, 2024 ended on a positive note in terms of the DGPP’s financial health. Its financial ratios have reached peaks in the last 20 years.
First, the funding ratio, which is a key indicator of the Plan’s ability to meet its obligations over the long term, went from 120% to 122%. This far exceeds the target level of the stabilization provision required under Quebec legislation since 2016, which is 113% as at December 31, 2024, for the DGPP. The solvency ratio, which assesses the DGPP’s ability to pay benefits if the Plan is terminated, went from 103% to 105%.
These excellent results can be attributed to our investment managers’ risk management practices and smart strategies, which have been in place for many years. They’re designed to ensure that every plan member receives the benefits they’ve been promised over the long term. The results are also owed to the sustained financial efforts of plan members and Desjardins Group employers in recent years.
On the back of the Plan’s strong financial performance, the Desjardins Group Board of Directors was able to approve a reduction in contributions for plan members and employers, while maintaining the same benefits. This reduction has been in effect since late 2024. This reduction means lower contribution amounts while ensuring that the Plan remains well funded for the future.
Ensuring the Plan’s long-term viability

Some of our key objectives include maintaining strong financial health and stable contributions over time.
To achieve them, DGPP actuaries continually assess the Plan’s future commitments using the most probable assumptions about events that could affect its financial health. They also include provisions in these assessments to cover unforeseen events. This ensures that the DGPP has the necessary resources to meet its long-term obligations and ensure financial stability.
2025 will be the first year where the benefits paid out by the DGPP will exceed Plan contributions. The DGPP has been in place since 1979, and it now has a significant number of retirees. We’ve been anticipating this situation for a number of years. Our management strategies take this change into account.
As such, we’re continuing to closely monitor economic and demographic factors that could affect the Plan’s financial health. Management decisions are made carefully to ensure that benefits are sustainable and that the DGPP is stable for all plan members and beneficiaries.